Understanding The Unitary System Of Government
What unitary system of government refers to a centralized form of governance where all powers and authority are concentrated in a single national government. Unlike federal systems, where power is shared between national and regional governments, a unitary system operates under a singular legal authority. This means that sub-national entities, such as states or provinces, derive their powers from the central government rather than having constitutionally guaranteed powers of their own. In this article, we will delve into the structure, advantages, and disadvantages of the unitary system of government.
Countries that adopt the unitary system often do so for the sake of efficiency and uniformity in governance. With a centralized authority, decision-making can be swift and cohesive, allowing for streamlined policies and regulations that apply to the entire nation. This can be particularly beneficial in smaller nations where regional disparities are minimal. However, this concentration of power can also lead to challenges, such as the potential for abuse of authority and neglect of local needs.
Throughout this article, we will explore various aspects of the unitary system of government, addressing common questions and concerns. From its historical context to its practical implications in contemporary governance, our goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of what unitary system of government entails.
What are the Characteristics of a Unitary System of Government?
A unitary system of government is defined by several key characteristics:
- Centralized Authority: The central government holds the majority of power.
- Uniform Laws: Laws and regulations are consistent across the entire nation.
- Delegated Powers: Local governments operate under authority granted by the central government.
- Lower Levels of Government: Regional or local governments exist but have limited autonomy.
How Does a Unitary System Differ from a Federal System?
The distinction between unitary and federal systems is crucial for understanding governance structures worldwide. In a federal system, power is divided between national and regional governments, allowing for greater local autonomy. Here are some fundamental differences:
- Power Distribution: In federal systems, constitutionally defined powers are shared, while unitary systems centralize authority.
- Legal Framework: Federal systems have multiple layers of laws, whereas unitary systems maintain uniform law across the nation.
- Local Governance: Local governments in federal systems can create their laws, while in unitary systems, they can only implement laws established by the central government.
What Countries Utilize a Unitary System of Government?
Many countries around the world adopt a unitary system of government. Some notable examples include:
- France
- Japan
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
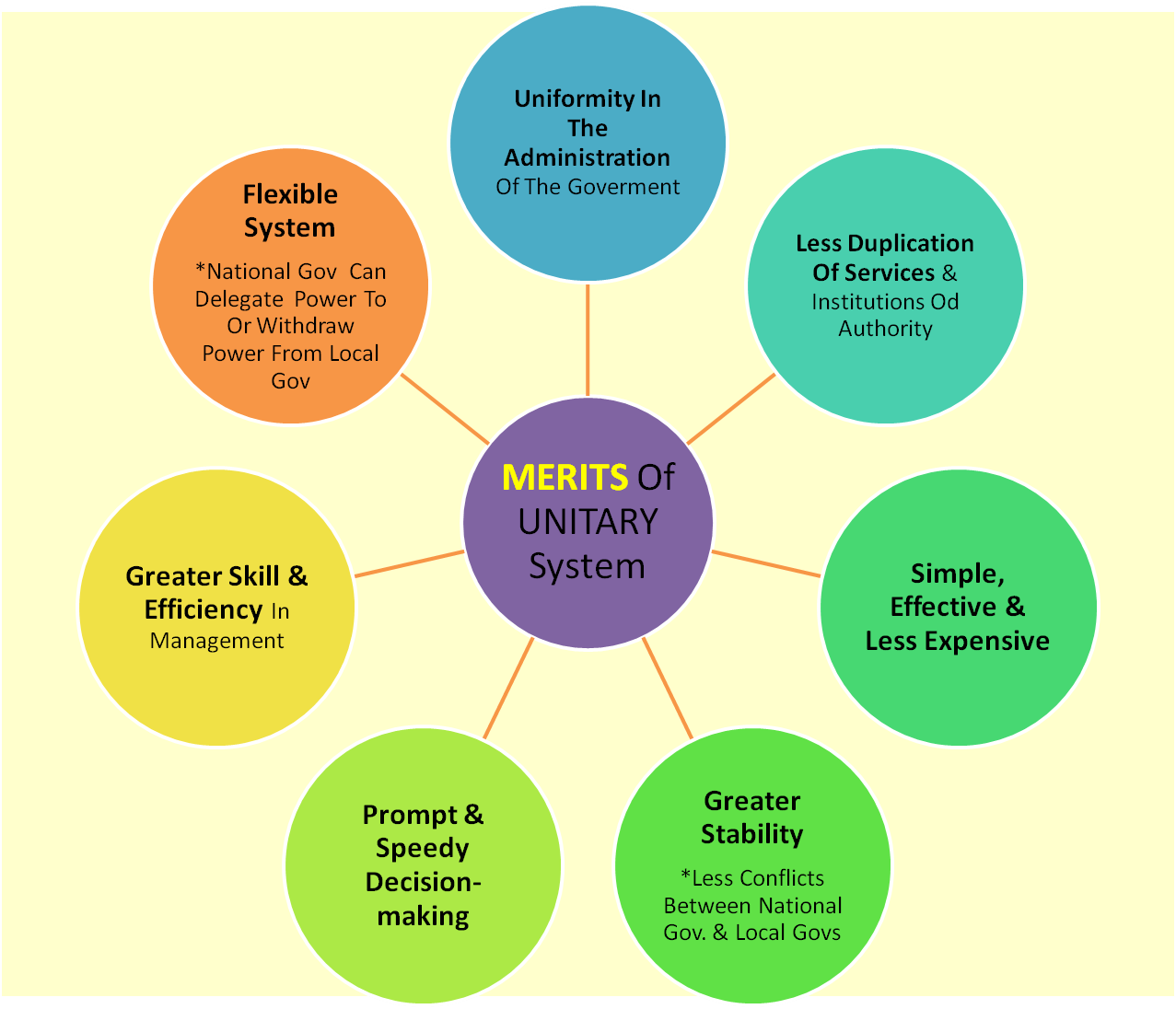
What are the Advantages of a Unitary System of Government?
The unitary system of government presents several advantages:
- Efficiency: Decision-making processes are streamlined, enabling swift responses to national issues.
- Consistency: Uniform laws create predictability and stability for citizens.
- Reduced Duplication: Centralized governance minimizes the chances of overlapping regulations and bureaucratic red tape.
What are the Disadvantages of a Unitary System of Government?
Despite its advantages, a unitary system also has notable disadvantages:
- Centralized Power: This structure can lead to authoritarianism if checks and balances are not properly instituted.
- Neglect of Local Needs: Centralized decision-making may overlook regional differences and local needs.
- Limited Local Autonomy: Local governments may struggle to address unique issues effectively.
Can a Unitary System Adapt to Local Needs?
While a unitary system is characterized by centralization, it can incorporate mechanisms for addressing local needs. For instance:
- Local governments can have advisory roles in decision-making.
- National policies may be tailored to accommodate regional disparities.
- Decentralized programs can be implemented to promote local governance.
Conclusion: The Role of the Unitary System of Government in Modern Governance
In summary, the unitary system of government is a pivotal model of governance that emphasizes centralized authority and uniformity in law. While it offers efficiency and consistency, the potential drawbacks necessitate careful consideration of local needs and checks on power. Understanding the intricacies of this system can provide valuable insights into how various nations function and the challenges they face in governance.
Unraveling The Origins: Where Was Gisele Bundchen Born?
Exploring The Vibrant Harmony: Does Purple And Red Go Together?
The Rising Stars: Celebrating Black Hallmark Actresses